Abigail Thomson, Alissa Wolfe, Isaac Davis, Zach Marcin
Service-Learning Project for Econ 432: Urban Economics
Faculty Advisor: Dr. Samia Islam
Introduction
The goal of this research is to understand communication systems that could be used to help advance civic engagement with the local government here in Boise.
As Boise develops economically it is imperative to incorporate the best technology into the community.
Literature Review
Source One:
Connecting citizens and local governments? Social media and interactivity in major U.S. cities, by Karen Mossberger, Yonghong Wu, Jared Crawford.
In Summary
- There are many communication mediums online but what network is best for communicating government information?
Source Two:
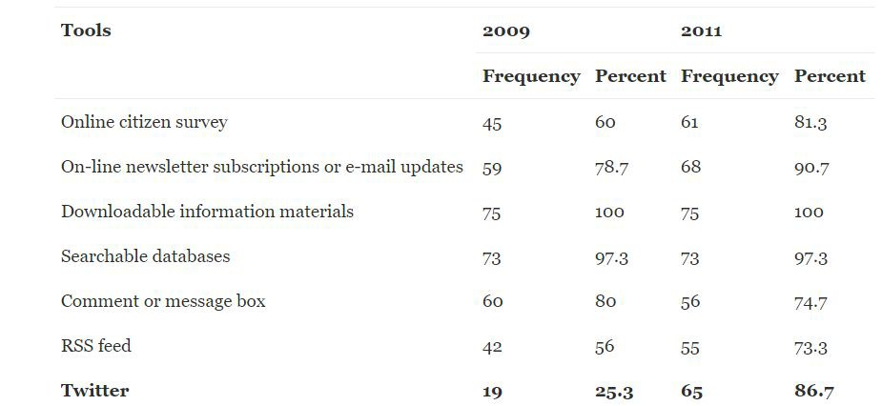
Citizens’ perceptions of the impact of information technology use on transparency, efficiency and corruption in local governments, by David Valle-Cruz, Rodrigo Sandoval Almazan, and J. Ramon Gil-Garcia.
In Summary
- Created to “explore the theoretical foundations and existing empirical studies related to the impact of information technology use on citizen perceptions of transparency, efficiency and corruption, considering citizens as users of government information and services.”
- Developed and tested a model in which the dependant variables are citizen perceptions of transparency, efficiency, and corruption.
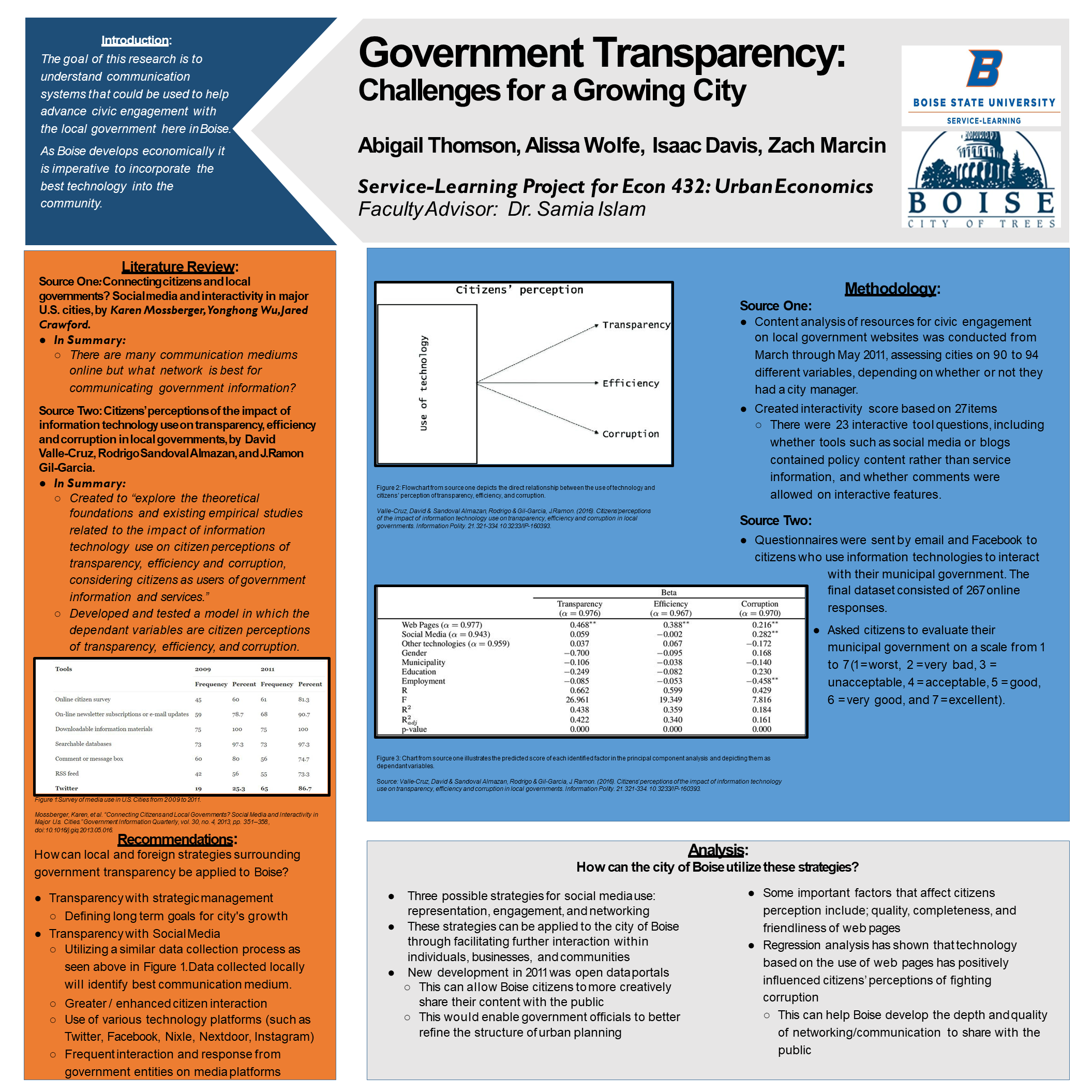
Mossberger, Karen, et al. “Connecting Citizens and Local Governments? Social Media and Interactivity in Major U.s. Cities.” Government Information Quarterly, vol. 30, no. 4, 2013, pp. 351–358., doi:10.1016/j.giq.2013.05.016.
Recommendations
How can local and foreign strategies surrounding government transparency be applied to Boise?
Transparency with strategic management
- Defining long term goals for city’s growth
Transparency with Social Media
- Utilizing a similar data collection process as seen above in Figure 1. Data collected locally will identify best communication medium.
- Greater / enhanced citizen interaction
- Use of various technology platforms (such as Twitter, Facebook, Nixle, Nextdoor, Instagram)
- Frequent interaction and response from government entities on media platforms
Methodology
Source One
Content analysis of resources for civic engagement on local government websites was conducted from March through May 2011, assessing cities on 90 to 94 different variables, depending on whether or not they had a city manager.
Created interactivity score based on 27 items
There were 23 interactive tool questions, including whether tools such as social media or blogs contained policy content rather than service information, and whether comments were allowed on interactive features.
Source Two
Questionnaires were sent by email and Facebook to citizens who use information technologies to interact with their municipal government. The final dataset consisted of 267 online responses.
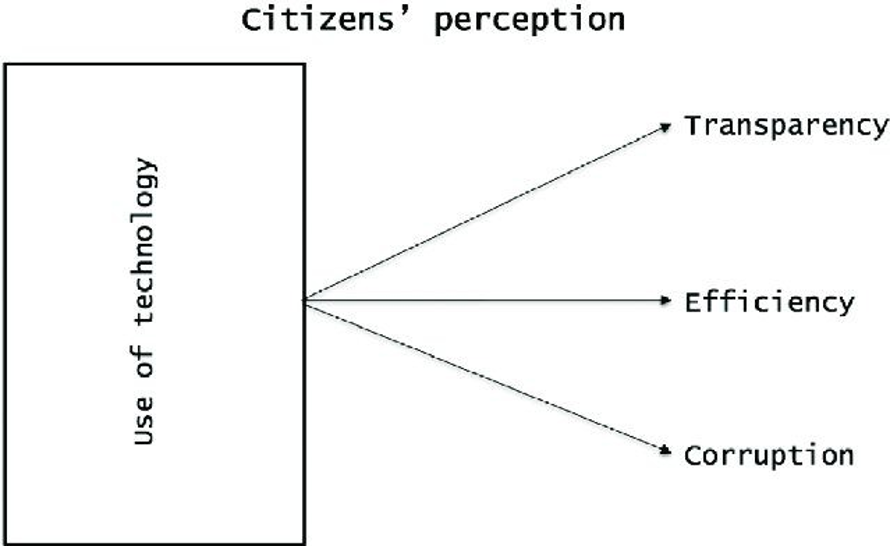
Asked citizens to evaluate their municipal government on a scale from 1 to 7 (1 = worst, 2 = very bad, 3 = unacceptable, 4 = acceptable, 5 = good, 6 = very good, and 7 = excellent).
Valle-Cruz, David & Sandoval Almazan, Rodrigo & Gil-Garcia, J. Ramon. (2016). Citizens’ perceptions of the impact of information technology use on transparency, efficiency and corruption in local governments. Information Polity. 21. 321-334. 10.3233/IP-160393.
Source: Valle-Cruz, David & Sandoval Almazan, Rodrigo & Gil-Garcia, J. Ramon. (2016). Citizens’ perceptions of the impact of information technology use on transparency, efficiency and corruption in local governments. Information Polity. 21. 321-334. 10.3233/IP-160393.
Analysis
How can the city of Boise utilize these strategies?
Three possible strategies for social media use: representation, engagement, and networking
These strategies can be applied to the city of Boise through facilitating further interaction within individuals, businesses, and communities. New development in 2011 was open data portals. This can allow Boise citizens to more creatively share their content with the public. This would enable government officials to better refine the structure of urban planning
Some important factors that affect citizens perception include; quality, completeness, and friendliness of web pages. Regression analysis has shown that technology based on the use of web pages has positively influenced citizens’ perceptions of fighting corruption. This can help Boise develop the depth and quality of networking/communication to share with the public
Additional Information
For questions or comments about this research, contact Alissa Wolfe at alissawolfe@u.boisestate.edu.