Associate Professor
Biochemistry
Email: henrycharlier@boisestate.edu
Office: SCNC 315
Phone: (208) 426-1391
Research Interests:
- Biochemistry
- Enzymology
- Protein Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
About Me
Undergraduate Research Assistant
What am I looking for in an undergraduate research assistant?
What courses would you recommend students have taken prior to working in your laboratory?
I do not require that students have any courses in chemistry to do research in my lab, but it would be helpful if they have taken general chemistry. Most important to me is that the student has a good work ethic and genuine interest in doing research. I want to see a “fire-in-the-belly” for trying research.
How many hours per week do you expect a student to spend in the laboratory per research credit and does the time have to be a set schedule?
For each research credit for which a student enrolls, there is an expectation of a minimum of 4 hours of work in the lab each week.
Ideally, for what length of time would a student research in your laboratory to achieve a meaningful research experience?
Students should expect to begin with training for the first 4 weeks before they will begin a project of their own.
Educational Background
1997-2000: Postdoctoral Fellowship Biochemistry | University of Iowa,
Subject of study: Kinetic cooperativity of human alcohol dehydrogenase.
Postdoctoral Mentor: Professor Bryce V. Plapp
1991-1996: Ph.D. Biochemistry | Medical College of Wisconsin
Doctoral Dissertation: Mechanistic Studies of Two Important Biosynthetic Enzymes: Phosphoribulokinase and 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase
Doctoral Mentor: Professor Henry M. Miziorko (retired)
1986-1991: B.S. Chemistry and Biology | University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point
Research Overview
My overall research interests involve the fields of enzymology and protein chemistry. Proteins are very interesting molecules that serve a variety of functions in living organisms. My current research involves studies in three areas which will be briefly described:
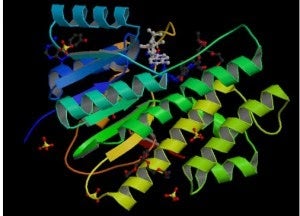
Carbonyl Reductase – Carbonyl reductase (CR), E.C. 1.1.1.184, catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide range of carbonyls. CR has been connected to several important processes including but not limited to quinone detoxification, neuroprotection, prostaglandin metabolism, and, of clinical interest, anthracycline metabolism. CR reduction of anthracyclines significantly impacts their use in the treatment of cancer as it has been linked to both drug resistance and cardiotoxicity mechanisms. Therefore, inhibition of CR in conjunction with anthracycline therapy offers the potential both to increase the effectiveness of the drugs and to decrease the risk of the associated cardiotoxicity. The major emphasis of this work is to better understand how CR recognizes the molecules to which it binds, be they substrates or inhibitors. Equipped with this information, drugs may be designed to control CR with the intention of reducing the risk of cardiotoxicity during anthracycline cancer treatment. Also, as the role of CR in other pathways is better understood such drugs may be used to treat other diseases as well. Pictured: Structure of human carbonyl reductase. Fromhttp://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1WMA
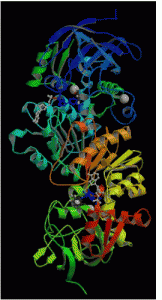
Alcohol Dehydrogenase – Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), E.C. 1.1.1.1, catalyzes the reversible oxidation of ethanol, using NAD as a cofactor. This reaction is a rate-limiting step in alcohol metabolism. ADH may be an important determinant in the development of alcoholism and fetal alcohol syndrome and is therefore widely studied. In addition, it often studied to gain insight into how enzymes catalyze reactions. My research project with ADH focuses on evaluating the contribution of electrostatic interactions in coenzyme binding. In past studies, a lysine at position 228 (K228) has been implicated in controlling, at least in part, coenzyme (NAD+ and NADH) binding. In particular, the positive charge at this position is hypothesized to interact with the negatively charged coenzymes. In order to evaluate the role of charge at position 228, we mutated the lysine at this position to alanine, glutamine, and glutamate, each of which changes the charge at this position. In a past study this lysine was also mutated to arginine, which conserves the positive charge at 228. Currently, all of these mutants are being analyzed for effects on coenzyme binding using steady state and transient kinetics, equilibrium binding studies, and computational chemistry. Pictured: Structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. From http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1HLD
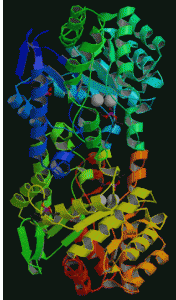
Phosphotriesterase – Phosphotiesterase (PTE), E.C. 3.1.8.1, catalyzes the hydrolysis of synthetic organophosphate triesters and phosphorofluoridates. Compounds in this family include several pesticides and nerve agents. This enzyme has potential use in nerve agent and pesticide decontamination. Work in my lab involves using protein chemistry and genetic engineering techniques to modify this enzyme to enhance its utility in organophosphate compound degradation. Pictured: Structure of bacterial phosphotriesterase. From http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1P6C
Funded Projects
STEM Education for All: Building a Vision for Sustaining Innovation and Prosperity.
Period: 9/01/09-8/31/11
Co Principle Investigator
Funding Agency: NSF-MSP Start Partnership
The goal of this grant is to collect data from several sources across Idaho to address STEM concerns in the state.
“Biophysical and Biochemical of Protein Structure and Interactions.”
Period: 7/01/05-6/30/07
Project Team Leader
$150,000
Funding Agency: Office of Research Administration, Boise State University.
“Structure/function analysis of anthracycline reduction by human carbonyl reductase.”
Period: 7/01/04-6/30/09
Magnet Principle Investigator.
My portion is for about $376,000
Funding Agency: NIH NCRR
This is a subproject of the Idaho-INBRE, NIH/NCRR P20-RR16454.
“Synthesis of doxorubicin C14 benzyl ethers and evaluation as carbonyl reductase substrates and topoisomerase II inhibitors.”
Period: 5/04 – 5/05
Co Principle Investigator
$5000
Mountain States Tumor and Medical Research Institute
Teaching Philosophy
I believe that students need to take responsibility for their own learning and my role is to be more of a learning coach than a lecturer. I try to provide opportunities for students to experience the material rather than to simply hear a lecture and memorize material. In my experience as a teacher and a student, I have found that if I haven’t developed an understanding of the fundamentals, I never learned the material and have forgotten it. My other belief is that one should work hard and play hard. I always try to build fun into the classroom, while at the same time I work hard to challenge each student and help them to achieve goals that they may not have thought possible.
Courses Taught
CHEM 111 – College Chemistry I
CHEM 112 – College Chemistry II
CHEM 350 – Fundamentals of Biochemistry
CHEM 431 – Biochemistry I
CHEM 432 – Biochemistry Laboratory
CHEM 433 – Biochemistry II
CHEM 286/386 – Seminar
CHEM 498 – Senior Seminar
CHEM 500 – Introduction to Chemical Research
BIOCHEM 510 – Advanced Protein Chemistry
BIOCHEM 512 – Intermediary Metabolism
CHEM 597 – Special Topics – Enzyme Kinetics
BMOL 602 – Biomolecules II
BMOL 605 – Current Scientific Literature
Peer Reviewed Publications
Plapp, B. V., Charlier, H. A., Ramaswamy, S. (2016) “Mechanistic implications from structures of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase complexed with coenzyme and an alcohol.” Archives of Chemistry and Biophysics 591:35-42.
Hilton, M., Gerasimchuk, N., Silchenko, S., Charlier, H. (2013) “Synthesis, Properties and Crystal Structure of the 2,4-Dichlorophenyl-cyanoxime: A Powerful Carbonyl Reductase Inhibitor.” J. Chem. Crystallography43:157-164.
Berhe S., Slupe A., Luster C., Charlier, Jr., H.A., Warner D.L., Zalkow L.H., Burgess E.M., Enwerem N.M., Bakare O. (2010) Synthesis of 3-[(N-carboalkoxy)ethylamino]-indazole-dione derivatives and their biological activities on human liver carbonyl reductase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 218(1):134-41.
Cusack, B.J., Gambliel, H., Musser, B., Hadjokas, N., Shadle, S., Charlier, H., Olson, R.D. (2006) “Prevention of Chronic Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity in the Adult and Aged Fischer 344 Rat by Dexrazoxane and Effects on Iron Metabolism”. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 58(4), 517-526.
Berhe S., Slupe A., Luster C., Charlier, Jr., H.A., Warner D.L., Zalkow L.H., Burgess E.M., Enwerem N.M., Bakare O. (2010) Synthesis of 3-[(N-carboalkoxy)ethylamino]-indazole-dione derivatives and their biological activities on human liver carbonyl reductase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 218(1):134-41.
Patents
Charlier, H. A. (2007) “Antitumor compositions containing anthracyclines and inhibitors of carbonyl reductase for reducing the cardiotoxicity of anthracyclines.” U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ., US 20070225238 A1 20070927.
Charlier, H. A., and Gerasimchuck, N. (2010) “Cyanooxime inhibitors of carbonyl reductase and methods of using said inhibitors in treatments involving anthracyclines.” US 7,727,967 B2
Charlier, H. A., and Ewing, C. (2010) “Biphenyl inhibitors of carbonyl reductase.” US 7,781,412 B2
Yu, G., Brown, E., Charlier, H. A. (2010) “Identifying and counting proteins in a sample.” U.S. Pat. Appl. Publ., US 20100062538 A1 20100311
Hobbies
I am an avid fisherman. My favorite style of fishing is fly fishing and my most productive fly is a #10 black wooly bugger with brown hackle. It catches everything from trout to bass to bluegill. I love to fish Idaho, Iowa, and Wisconsin. This wooly bugger is effective in each state. I should mention that I also love to fish with muddler minnows. I have used this fly to catch nearly all species of trout and in Wisconsin have caught both smallmouth bass and walleyes. I even caught a catfish with it. My other productive flies include the cattertail, stayner ducktail, and stimulator.
As of June 2021, I am the current holder of the Idaho state record carp (34 pounds). I have been using European methods for targeting carp and this record fish was caught with the following:
- Pack bait: Panko breadcrumbs, oatmeal, canned cream corn, canned corn, and strawberry Jell-O.
- Hook bait: Pineapple ice cream flavored boilie. Flavoring was purchased from the Wicked Carp Company.