The Boise Hydrogeophysical Research Site (BHRS) is a wellfield developed in a shallow, coarse (cobble-and-sand), alluvial aquifer with the goal of developing cost-effective methods of quantitatively characterizing the distribution of permeability in heterogeneous aquifers using hydrologic and geophysical techniques. Responses to surface geophysical techniques (e.g., seismic, radar, transient electromagnetics) can be calibrated against a highly characterized control volume (the wellfield) with 3-D distributions of geologic, hydrologic, and geophysical properties determined from extensive field measurements. Also, these data sets will be used to investigate relationships between properties and to test petrophysical models.
Design
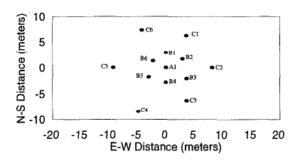
Well coring and construction methods, and the well arrangement in the filed, are designed to provide detailed control on lithology and to support a variety of single-well, crosshole, and multi-well geophysical and hydrologic tests. The central area of the wellfield has a double-ring pattern with a central well surrounded by two rings of six wells each. Wells are screened through the cobble-and-sand aquifer to a clay layer that underlies the BHRS at about 20 m depth. In addition, the wellfield design optimizes well-pair distances and azimuths for determination of short range geostatistical structure.